In times of market volatility, like crashes or bubbles, many clients want to sell securities urgently and withdraw funds quickly. During strong economic growth, companies tend to have higher revenues and profits. Investors tend to sell shares of companies with weak liquidity if a recession is expected.
Everything You Need To Master Financial Modeling
For example, suppose a company has Rs.50,000 in cash, Rs.20,000 in T-bills, and Rs.100,000 in accounts payable; its cash ratio would be as given below. Although examining organizations’ profitability and efficiency is crucial, liquidity risks remain very real and serious, as demonstrated by the 9/11, Lehman, and COVID crises. We then divide the quick assets by the average daily cash expense to obtain the number of days those quick assets can cover. Like activity and ROI ratios, the defensive interval takes items from the Balance Sheet and the Income Statement.
Who Uses Liquidity Ratios?
The cash ratio is the most stringent liquidity ratio, focusing only on the company’s cash and cash equivalents to cover its short-term liabilities. A higher cash ratio indicates a stronger financial position, but it may also suggest inefficient use of cash resources. Evaluating liquidity through current, quick, and cash ratios provides vital insights into a company’s financial health and flexibility. Assessing liquidity trends over time and against competitors allows stakeholders to identify improving or deteriorating liquidity. With a comprehensive understanding of these fundamental ratios, financial analysts and managers can better monitor short-term financial performance. Some are fixed in nature and then there are current assets and current liabilities.
- Apple had $63.9 billion of funds available in total for the immediate payment of short-term debt.
- It may be advantageous for a company to reduce its cash ratio in these cases.
- On the other hand, if a company has high financial obligations and limited assets to cover those costs, it would have a high solvency ratio but lower liquidity.
- Since the Current Ratio of Sprouts is 1.290, we should expect their Net Working Capital to be positive.
- When converting assets into cash or cash equivalents, firms should do so at a fair market price.
Navigating Financial Waters: Exploring the Intersection of Algorithmic Trading and Market Liquidity Dynamics
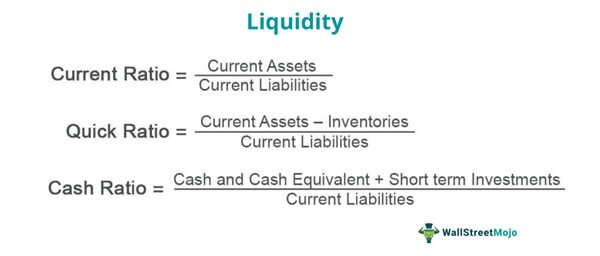
Accounts receivable represents goods or services that have already been sold and will typically be paid/collected within 30 to 45 days. As opposed to the Current Ratio, the Net Working Capital Ratio puts more emphasis on current liabilities. It is calculated by taking a company’s total current assets minus its total current liabilities. A higher ratio indicates that the company has enough liquid assets to cover all its short-term debt obligations without selling any other assets. The cash ratio is the most stringent of all Liquidity Ratios and measures a company’s ability to pay off its short-term debt with only cash or cash equivalents.
Comparing Liquidity Ratios
As such, it is generally recommended that companies review both ratios to assess their financial health and liquidity position accurately. The credit institution shall notify the competent authority of that outflow no later than the submission of the reporting in accordance with Article 415 of CRR. The credit institution shall apply a 100% outflow rate to those additional collateral or cash outflows.
What are three types of liquidity ratios?
They provide insight into a company’s ability to repay its debts and other liabilities out of its liquid assets. The quick (acid-test) ratio is considered the most stringent since it excludes inventory from current assets before dividing by current liabilities. This provides insight into whether or not a company can meet short-term obligations without relying on inventory sales.
The company has more cash and cash equivalents than current liabilities when its cash ratio is greater than one. It can cover all short-term debt and still have cash remaining in this situation. Yes, a accounting for convertible bonds and debt with examples current ratio of 2 is typically considered a good level of liquidity. It means the company has twice as many current assets as current liabilities, demonstrating good short-term financial flexibility.
However, unless the financial system is in a credit crunch, a company-specific liquidity crisis can be resolved relatively easily with a liquidity injection (as long as the company is solvent). Credit institution shall use the formulae laid down in this Annex to determine the composition of their liquidity buffer in accordance with Article 17. It shall only be possible to draw on such facilities following the reasonably expected demand for a promotional loan and up to the amount of such demand provided there is a subsequent reporting on the use of the funds distributed. Deposits received as collateral shall not be considered as liabilities for the purposes of Article 24, 25, 27, 28 or 31a but shall be subject to the provisions of paragraphs 1 to 6 of this Article, where applicable. The amount of cash received exceeding the amount of cash received as collateral shall be treated as deposits in accordance with Article 24, 25, 27, 28 or 31a.
A quick ratio of 1.3 means the company has Rs.1.30 of highly liquid assets available to cover each Rs.1 of current liabilities. This indicates it is in a strong position to meet its short-term obligations without needing to sell inventory or other assets. Low liquidity raises risks of defaulting on loans, disrupting cash flows, or halting operations.
A higher liquidity ratio indicates a company is more liquid and has a greater ability to meet its short-term obligations. A liquidity ratio below 1 means a company’s current liabilities exceed its current assets, and it has trouble meeting short-term obligations if current assets cannot be quickly converted to cash. However, the Ratio cannot go negative as the assets and liabilities are not negative values. Even if a company has zero current assets, the ratio ratio would be 0, which is not a negative number.
A 1.1 ratio means the company has enough cash to cover current liabilities. This takes an even closer look at the liquidity situation, as only the most liquid funds are compared to the current liabilities. These are the liquid funds that are available to the company very quickly, which is an advantage if an unexpected higher sum has to be paid at short notice. There are different liquidity ratios, so there are also different formulas.
